The Linux Command line interface(0)
See all writings || Archive
I spend 90% of my time in the Terminal emulator (not really sure about that tho), for me it offer's great flexibility and control than the GUI, and it can be really intimidating at first but it worth your time.
Prerequisites: unix or unix-like operating system.
Goals:
- Learn what a command line is and how to use it
- Learn common useful commands and what they mean
What a command line interface?
when talking about the command line we are actually refering to The Shell. The shell is a program that takes in Commands or #keywords and passes them to the operating system to carry out. it's a way of interacting with the computer os, similiar to the GUI but faster and more powerful. The program which handles this commands in the terminal emulator is the Command-line interpreter (shell).
Shell Scripting:
As earlier said a Unix shell or shell is a command-line interpreter but also a programming language, the programming language features allows us to combine commands or (utilities) together in a file and run them as a scripts, and yea you can also call it a Script language for now the major focus is getting you to understand the command line and having the feels of it without getting intimidated.. will write more on Shell script on Using The Linux Command Line(1) or probably the next.
Running the Termainal emulator:

Before delving into what the Terminal emulator actually is, it's important to know where it all started decades ago. Computers had no GUI for accessing or modifying data; the computer terminal was the only means of entering, displaying, and printing data. These terminals were physical computing devices like IBM 3270, VT100, and many others. For more details, check out computer terminal >> wiki.
What's a Terminal emulator: The Terminal emulator is a software designed to replicate the functions of a computer terminal. It is a GUI application needed to access the Unix shell environment, providing an interface to invoke commands, scripts, and programs available on your system. It also allows you to view and browse through the contents of directories, just like you would with a FILE MANAGER APPLICATION.
Every Linux distro comes with a default terminal emulator. For instance, Ubuntu and Fedora come with Gnome terminal emulator, and other Linux distros have their own defaults. The first thing you see in the terminal emulator is the "command prompt," which shows $, %, #, or >, indicating the current working directory, the current user, and the readiness of the shell to accept commands from you.
The default shell for most Unix or Unix-like systems is the bash shell. Other shells include sh, zsh, csh, and more. To find out the available shells on your system, use the command:
cat /etc/shellsDisplay content in your file directory
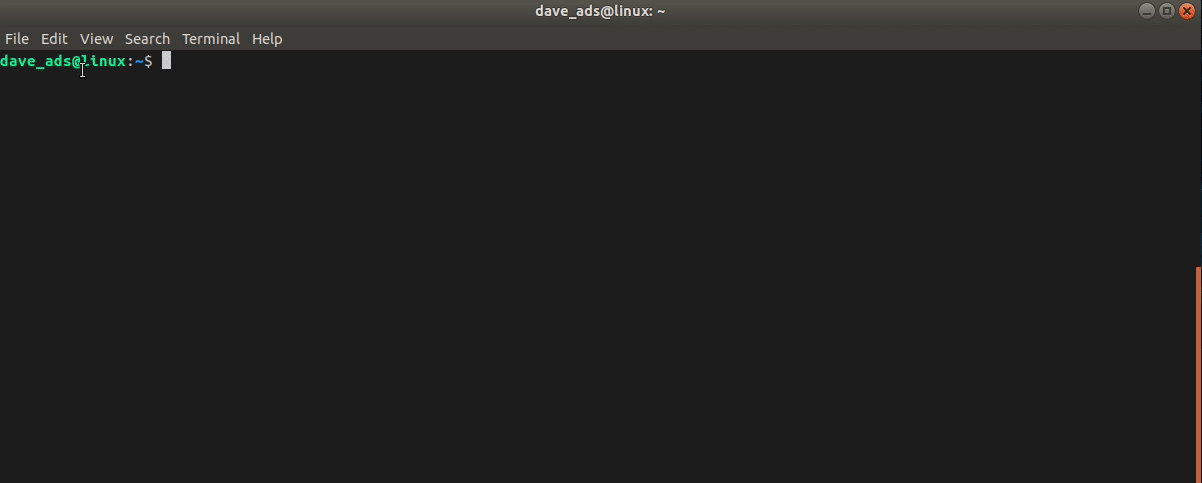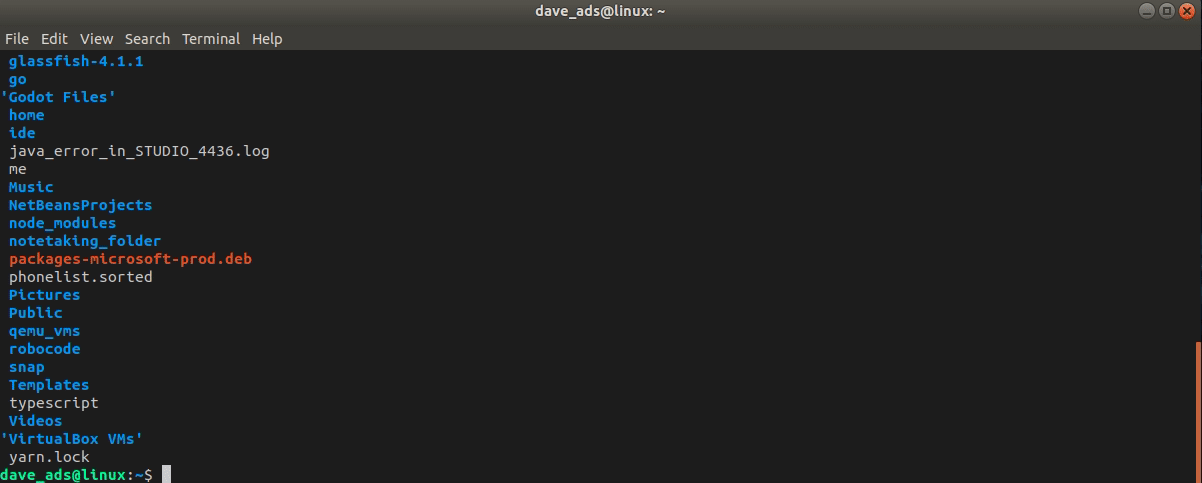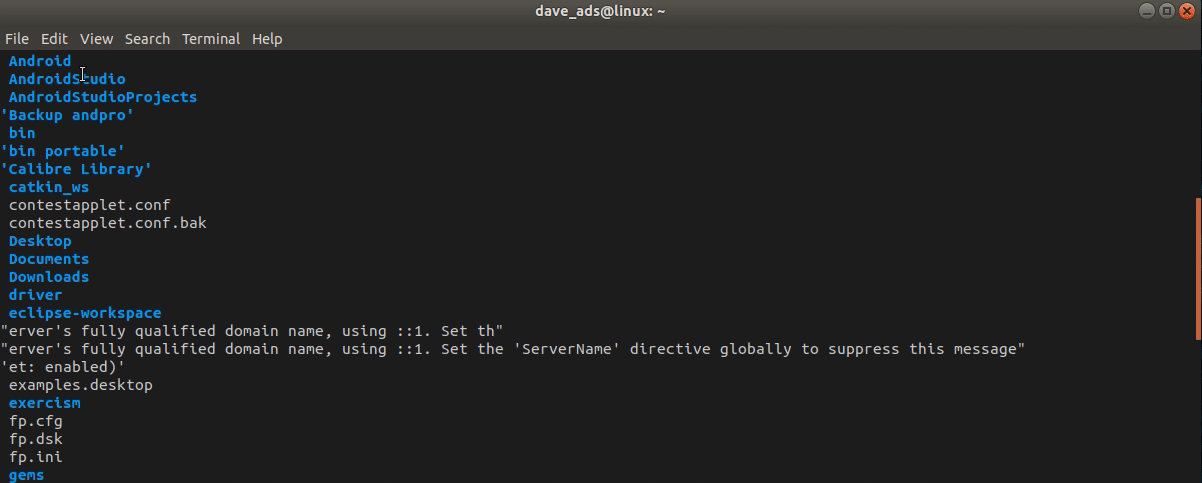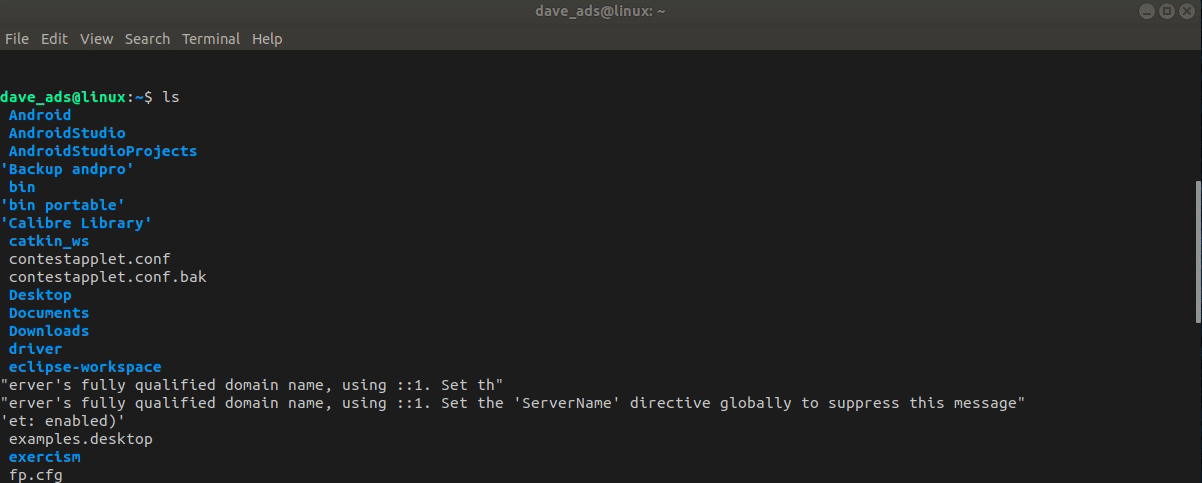
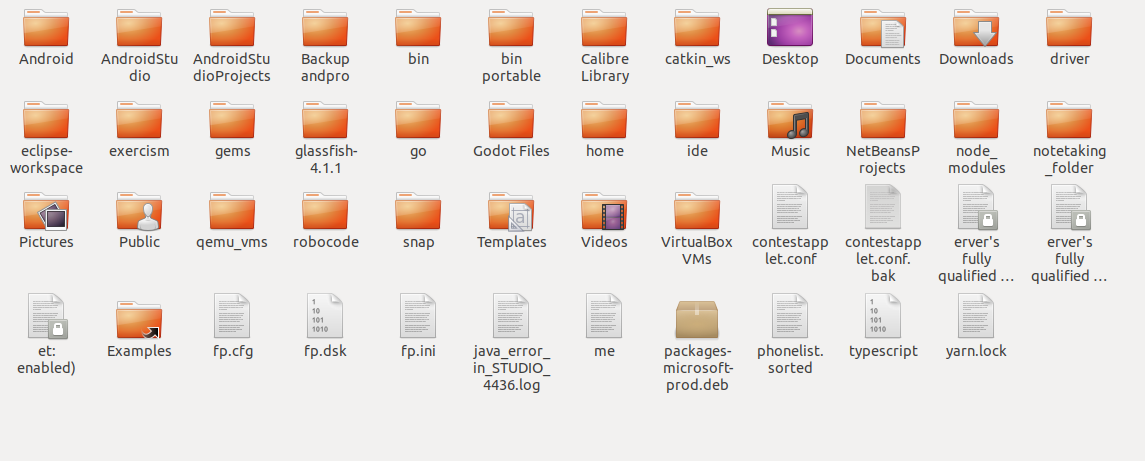
The ls command is used to print out the current directory on the terminal emulator screen, giving the same result as the File Manager.
To find out what a command means through the command line, type:
whatis lsYou can also make use of the system's manual pager for the full documentation:
man lsTo print your current working directory, use the command pwd.
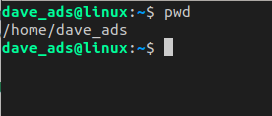
The pwd is a built-in command within the bash shell itself. Type help to find out more about built-in commands.
Time for Experiments
Here are some common commands:
| Command | Meaning |
|---|---|
ls | List files and directories in the current directory. |
cd | Change the current working directory. |
pwd | Print the current working directory. |
mkdir | Create a new directory (folder). |
rmdir | Remove a directory (folder). |
cp | Copy files or directories. |
mv | Move or rename files or directories. |
rm | Remove (delete) files or directories. |
cat | Concatenate and display file content. |
more | Display file content one screen at a time. |
less | Display file content with backward navigation. |
head | Display the beginning lines of a file. |
tail | Display the ending lines of a file. |
grep | Search for a pattern in files. |
find | Search for files and directories. |
chmod | Change file permissions. |
chown | Change file ownership. |
ps | Display information about running processes. |
kill | Terminate processes. |
ssh | Secure Shell - remote login to a server. |
wget | Download files from the web. |
tar | Archive files using tar. |
zip | Package and compress files. |
Please note that this is not an exhaustive list, but it includes some commonly used commands and their primary meanings. Additionally, the meaning of some commands may vary based on their options and arguments. Always refer to the manual (man command) for a comprehensive understanding of each command.